Cisco
The added value
Cisco is a leading provider of enterprise cybersecurity solutions, offering a wide range of solutions that cover network, cloud, endpoint, and identity security. Cisco's strength lies in combining networking and security, helping organizations gain clear visibility into their systems, apply consistent security policies, and respond to threats quickly across mixed network environments. This approach improves security and makes management easier through a unified ecosystem.
Integrating the ESET PROTECT Platform with Cisco XDR enables users to pull detection and incident data using the ESET API and import it to Cisco XDR via the Cisco Private-Intel API. The app pulls newly created incident and detection data from the ESET PROTECT Platform. Detection data is transformed to Sightings (Events) and Judgments. To learn more about Modeling Threat Intelligence in CTIM (Cisco Threat Intelligence Model), refer to the CTIM Model tutorial on GitHub.
The pulled Incidents, as well as Events and Judgments, are available in Cisco XDR UI.
Integration type
•API-based integration
How to enable the integration
Ensure you meet prerequisites and follow the steps below to set up the ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app.
Prerequisites
•You have created the API user account.
•You have access to Cisco XDR as an administrator.
•You have created the Cisco API Client with a minimum scope of privileges—Private Intel (Access Private Intelligence), and saved the Client ID and the Client Password.
•You have installed Docker on the server where you want to set up the integration app.
•You have installed Docker Compose on the server where you want to set up the integration app.
The ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration was prepared and tested with Ubuntu 22.04.5. |
Integration configuration steps
The ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app is available for download on GitHub. See the latest integration app version under Releases on the GitHub page. |
Before running the installation commands, set the INTEGRATION_PATH environment variable to specify the path to the installation directory of your choice; for example, export INTEGRATION_PATH="/usr/local/integrations". The installation steps use this environment variable, so you do not need to specify the path in every command. |
1.Log in to the server where you want to set up the the ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app and download the app. Specify the latest app version, for example, 1.0.0, in the following command:
git clone --branch 1.0.0 https://github.com/eset/ESET-Integration-Cisco.git "$INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco" |
2.Create the .env file in the integration app folder, $INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco, or set the required variables in the environment:
•CISCO_XDR_API_CLIENT_ID—The Client ID of your Cisco API Client, which you have previously created and saved
•CISCO_XDR_API_CLIENT_PASSWORD—The Client Password of your Cisco API Client, which you have previously created and saved
•CISCO_XDR_API_REGION—The region of the Cisco XDR API you are using; the options are: eu, us, apjc.
•EP_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Cisco uses to pull detections and incidents; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET PROTECT subscription.
•EI_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Cisco uses to pull detections and incidents; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET Inspect subscription.
•ECOS_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Cisco uses to pull detections and incidents; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET Cloud Office Security subscription.
•INTERVAL—The time interval (in minutes) for the app to run and pull detections and incidents; the minimum value is three.
•INSTANCE_REGION—The location of your ESET PROTECT/ESET Inspect/ESET Cloud Office Security server; the options are: ca, de, eu, jpn, us.
•USERNAME_INTEGRATION—The API user's email
•PASSWORD_INTEGRATION—The API user's password
To create the .env file in the $INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco folder, use the following command:
touch "$INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco/.env" |
To edit the .env file, use an editor of your preference. In the following example, the nano text editor is used:
nano "$INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco/.env" |
Refer to the example of the .env file contents:
CISCO_XDR_API_CLIENT_ID=client ID CISCO_XDR_API_CLIENT_PASSWORD=client password CISCO_XDR_API_REGION=eu EP_INSTANCE=yes EI_INSTANCE=no ECOS_INSTANCE=yes INTERVAL=10 INSTANCE_REGION=eu USERNAME_INTEGRATION=email PASSWORD_INTEGRATION=password |
3.Build and run the ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app using the Docker Compose command:
docker compose --file "$INTEGRATION_PATH/ESET-Integration-Cisco/docker-compose.yml" up -d --build --force-recreate |
Integration verification
After configuring the integration, you can see the running app logs.
1.Use the following command to show all the running containers. Find the ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app container and copy its name:
docker ps |
2.Use the following command to show the running ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app logs; paste the container name copied in the previous step:
docker logs -f <docker container name> |
Additionally, review the newly pulled incidents in Cisco XDR > Incidents:
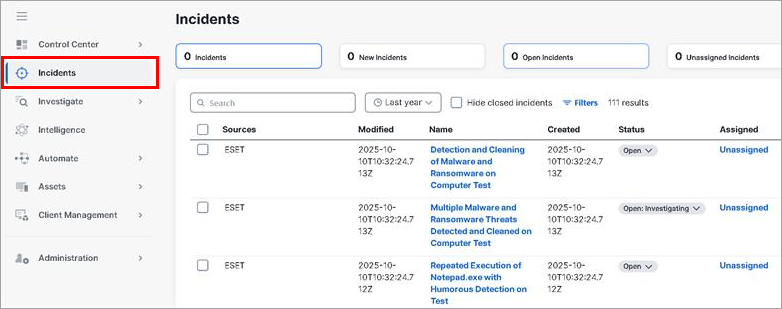
Review detections transformed to Sightings (Events) in Cisco XDR > Intelligence > Events > Private:
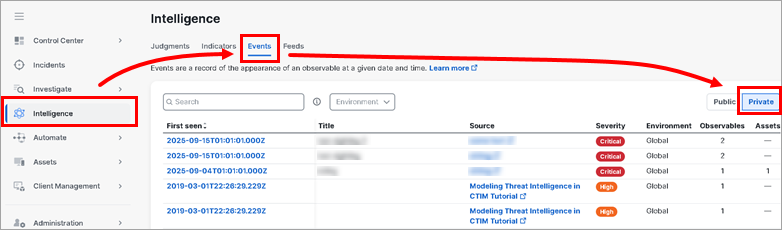
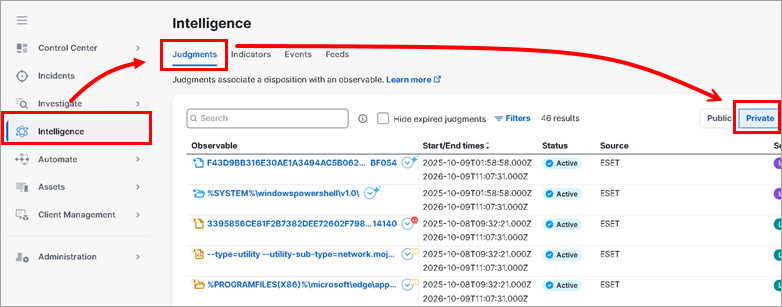
Review detections transformed to Judgments based on the identified observables using the Modeling Threat Intelligence in CTIM in Cisco XDR > Intelligence > Judgments > Private:
Troubleshooting
If you experience an issue with the integration, reach out to the local Partner in the respective country/region where you purchased your ESET subscription, or the respective ESET office, by opening a support request via the support form.
Ensure to include the required details from the list; they will help the support agent investigate the issue:
•Your API username
•Logs from the ESET PROTECT Platform and Cisco integration app container