Wazuh
The added value
Wazuh is an open-source security platform that combines Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) capabilities. It collects, aggregates, and analyzes security data from endpoints, servers, cloud environments, and network devices to detect and correlate potential threats.
Wazuh provides such features as threat detection, incident response, vulnerability assessment, configuration monitoring, compliance auditing, and centralized log management.
Integrating the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh enables users to ingest the detection data from ESET PROTECT, ESET Inspect and ESET Cloud Office Security, and incident data from ESET Inspect, to Wazuh. The data is pulled from the ESET public API with the time interval specified by the user and saved into a log file on the Wazuh side.
Integration type
•API-based integration
How to enable the integration
Ensure you meet prerequisites and follow the steps below to set up the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration on your Wazuh machine.
Prerequisites
•You have created the dedicated API user account.
•You have installed Wazuh with the following components: Wazuh manager, Wazuh indexer and Wazuh dashboard.
•You have installed Docker on the Wazuh machine.
•You have installed Docker Compose on the Wazuh machine.
The ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration was prepared and tested using the Virtual Machine OVA with Wazuh 4.10.1. |
Integration configuration steps
The ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app is available for download on GitHub. See the latest integration app version under Releases on the GitHub page. Refer to the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration update topic to learn how to update the integration to the latest version. |
1.Log in to the server console where Wazuh is running and download the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app; sudo privileges are required, as they enable you to run commands as the root user. Specify the latest app version, for example, 1.2.2, in the following command:
git clone --branch 1.2.2 https://github.com/eset/ESET-Integration-Wazuh.git /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh |
2.Copy the eset_local_rules.xml file to the /var/ossec/etc/rules folder. The file contains custom rules for Wazuh to identify the ESET detections. Wazuh uses the MITRE ATT&CK framework to detect, analyze, and respond to cyber threats by mapping security events to known attack techniques. Custom rules from the eset_local_rules.xml file enable Wazuh to interpret the ESET detections and map most of them to MITRE categories. Additionally, the eset_local_rules.xml file contains rules that help Wazuh interpret those ESET detections that are not mapped to MITRE.
cp /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh/eset_local_rules.xml /var/ossec/etc/rules/ |
3.Create the /var/log/eset_integration.log file that will store the ESET detections pulled by the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app:
touch /var/log/eset_integration.log |
4.Set up Wazuh to read logs saved in /var/log/eset_integration.log. Edit the /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf file by adding the /var/log/eset_integration.log path within the <ossec_config> tag under other local files configuration, as in the following example, and save the changes:
<ossec_config>
<!--Configuration of other local files -->
<localfile> <log_format>json</log_format> <location>/var/log/eset_integration.log</location> </localfile>
</ossec_config> |
To edit the /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf file, use an editor of your preference. In the following example, the nano text editor is used:
nano /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf |
5.Restart the server to apply the changes made in step 4:
systemctl restart wazuh-manager |
6.Create the .env file in the integration app folder, /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh, or set the required variables in the environment:
•EP_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Wazuh uses to pull detections; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET PROTECT subscription.
•EI_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Wazuh uses to pull detections; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET Inspect subscription.
•ECOS_INSTANCE—The ESET application that Wazuh uses to pull detection; the options are yes/no. Set yes if you have an ESET Cloud Office Security subscription.
•INTERVAL—The time interval (in minutes) for the app to run and pull detections, the minimum value is three. On the first and subsequent runs, until at least one detection record is pulled and saved, the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app retrieves the data whose occurrence time is later than the current time minus the specified time interval. For example, if the interval is set to 10, the app fetches the data from the past 10 minutes. When at least one detection record is pulled and saved, on the subsequent run, the app will pull detections whose occurrence time is later than the occurrence time of the most recently saved detection record.
•INSTANCE_REGION—The location of your ESET PROTECT/ESET Inspect/ESET Cloud Office Security server; the options are: ca, de, eu, jpn, us.
•USERNAME_INTEGRATION—The API user's email
•PASSWORD_INTEGRATION—The API user's password
To create the .env file in the /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh folder, use the following command:
touch /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh/.env |
To edit the .env file, use an editor of your preference. In the following example, the nano text editor is used:
nano /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh/.env |
Refer to the example of the .env file contents:
EP_INSTANCE=yes EI_INSTANCE=no ECOS_INSTANCE=yes INTERVAL=10 INSTANCE_REGION=eu USERNAME_INTEGRATION=email PASSWORD_INTEGRATION=password |
7.Build and run the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app using the Docker Compose command:
docker compose --file /var/ossec/integrations/ESET-Integration-Wazuh/docker-compose.yml up -d --build --force-recreate |
To prevent storage overload, we recommend that you move the log data to an archive and clean up the eset_integration.log file or use a different data retention and management method. |
Integration verification
After configuring the integration, you can see the running app logs.
1.Use the following command to show all the running containers. Find the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app container and copy its name:
docker ps |
2.Use the following command to show the running ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app logs; paste the container name copied in the previous step:
docker logs -f <docker container name> |
Additionally, you can see the most recently pulled ESET detections in the eset_integration.log file by running the following command:
tail -n 100 /var/log/eset_integration.log |
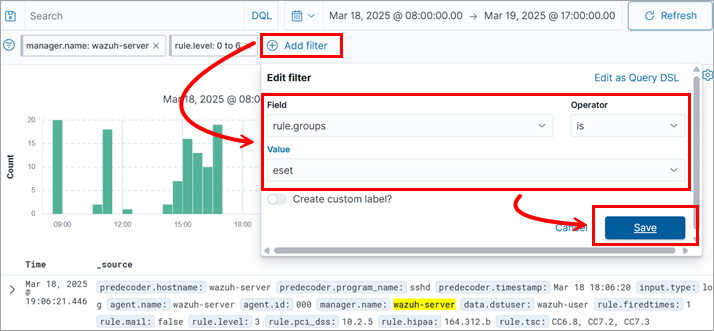
Alternatively, you can see the most recently pulled ESET detections in the Wazuh dashboard, which enables you to filter out the ESET logs.
1.In the Wazuh dashboard, click Add filter.
2.Edit the filter by setting the values:
•Field—rule.groups
•Operator—is
•Value—eset
3.Click Save.
Troubleshooting
If you experience an issue with the integration, reach out to the local Partner in the respective country/region where you purchased your ESET subscription, or the respective ESET office, by opening a support request via the support form.
Ensure to include the required details from the list; they will help the support agent investigate the issue:
•Your ESET Connect API username
•Logs from the ESET PROTECT Platform and Wazuh integration app container