Forwarding
ESET Internet Security can automatically send notification emails if an event with the selected verbosity level occurs. Open Advanced setup > Notifications > Forwarding and enable Forward notifications to email to activate email notifications.
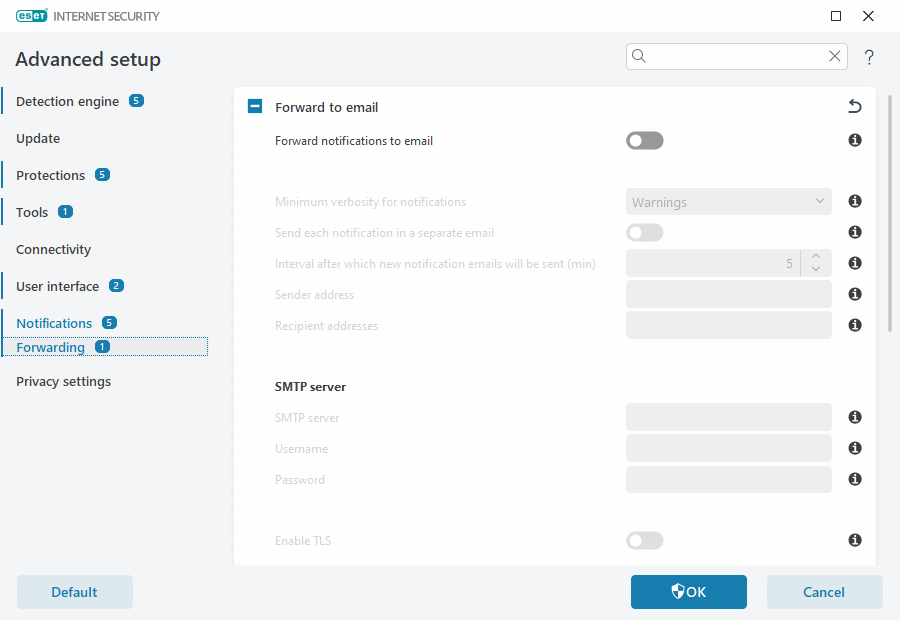
From the Minimum verbosity for notifications drop-down menu, you can select the starting severity level of notifications to be sent.
•Diagnostic—Logs information needed to fine-tune the program and all records above.
•Informative—Records informative messages such as non-standard network events, including successful update messages, plus all records above.
•Warnings—Records critical errors and warning messages (for example, update failed).
•Errors—Errors (for example, Document protection not started) and critical errors will be recorded.
•Critical—Logs only critical errors (for example, Error starting antivirus protection, or Threat found).
Send each notification in a separate email—When enabled, the recipient will receive a new email for each notification. This may result in many emails received in a short period.
Interval after which new notification emails will be sent (min)—Interval in minutes after which new notifications will be sent to email. If you set this value to 0, the notifications will be sent immediately.
Sender address—Define the sender address displayed in the header of notification emails.
Recipient addresses—Define the recipient addresses displayed in the header of notification emails. Multiple values are supported. Use semi-colon as the separator.
SMTP server
SMTP server—The SMTP server used for sending notifications (for example, smtp.provider.com:587, pre-defined port is 25).
SMTP servers with TLS encryption are supported by ESET Internet Security. |
Username and password—If the SMTP server requires authentication, these fields should be filled in with a valid username and password to access the SMTP server.
Enable TLS—Secure Alert and notifications using TLS encryption.
Test SMTP connection—A test email will be sent to the recipient's email address. SMTP server, Username, Password, Sender address, and Recipient addresses need to be filled in.
Message format
Communications between the program and a remote user or system administrator are done via emails or LAN messages (using the Windows messaging service). The Use default message format for the alert messages and notifications will be optimal for most situations. In some circumstances, you may need to change the message format of event messages.
Format of event messages—Format of event messages displayed on remote computers.
Format of threat warning messages—Threat alert and notification messages have a pre-defined default format. We recommend keeping the pre-defined format. However, in some circumstances (for example, if you have an automated email processing system), you may need to change the message format.
Charset—Converts an email message to the ANSI character encoding based on Windows Regional settings (for example, windows-1250, Unicode (UTF-8), ACSII 7-bit, or Japanese (ISO-2022-JP)). As a result, "á" will be changed to "a" and an unknown symbol to "?".
Use Quoted-printable encoding—The email message source will be encoded to Quoted-printable (QP) format, which uses ASCII characters and can correctly transmit special national characters by email in 8-bit format (áéíóú).
•%TimeStamp%—Date and time of the event
•%Scanner%—Module concerned
•%ComputerName%—Name of the computer where the alert occurred
•%ProgramName%—Program that generated the alert
•%InfectedObject%—Name of the infected file, message, etc.
•%VirusName%—Identification of the infection
•%Action%—Action taken over infiltration
•%ErrorDescription%—Description of a non-virus event
The keywords %InfectedObject% and %VirusName% are only used in threat warning messages, and %ErrorDescription% is only used in event messages.
